Abstract
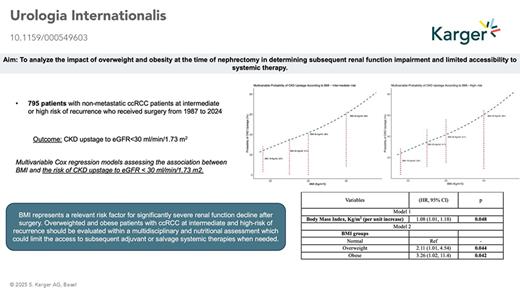
Introduction: Adjuvant or salvage systemic therapy after nephrectomy for intermediate- and high-risk clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) improves overall survival. However, severe renal impairment represents a relative contraindication to systemic therapy administration. This study aimed to analyze the impact of overweight and obesity at the time of nephrectomy in determining subsequent renal function impairment and limited accessibility to systemic therapy. Methods: Within a prospectively maintained database, we identified 795 nonmetastatic ccRCC patients at intermediate or high risk of recurrence. BMI was calculated as weight/height (kg/m2), and chronic kidney disease (CKD) upstage was defined as estimated glomerular filtration rate <30 mL/min/1.73 m2. Multivariable Cox regression models assessed the association between BMI and the risk of CKD upstage. Cumulative incidence curves illustrated the risk of disease relapse across different risk groups. Results: Overall, 504 (63%) were classified as intermediate and 291 (37%) as high risk of recurrence. The median BMI was 26 kg/m2 (IQR: 24–28), with 407 (51%) patients being overweight and 89 (11%) classified as obese. The 5-year risk of disease recurrence was 20% for intermediate and 70% for high-risk patients (p < 0.001). After accounting for patient, surgical, and tumor characteristics, the adjusted risk of CKD upstage increased from 24%–35% to 42%–61% in normal vs. overweight vs. obese patients. BMI resulted as an independent predictor of CKD upstage (hazard ratio [HR] 1.08, p = 0.04). Specifically, overweight (HR: 2.11) and obese (HR: 3.26) patients were at higher risk of CKD upstage (all p < 0.05). Conclusion: BMI emerges as an important marker of vulnerability to clinically meaningful postoperative renal function decline. Patients with intermediate- or high-risk ccRCC who are overweight or obese may benefit from structured multidisciplinary evaluation, including nutritional assessment, to preserve renal reserve and maintain eligibility for adjuvant or salvage systematic treatments when indicated.